Basic HTML Version
139
IBRACON Structures and Materials Journal • 2012 • vol. 5 • nº 2
D.V. RIBEIRO
| J.A. LABRINCHA
|
M.R. MORELLI
as fine sand. The gravel has a specific gravity of 2.74 kg/dm
3
and
maximum dimension of 19 mm.
The red mud was received in the form of a paste containing about
40% free water. In the present study, the material was dried and
crushed, and then used as a powdered additive. Ideally, if its po-
tential as a constituent of concrete is confirmed, red mud should
be incorporated and tested in the as-received condition, and the
free water present in the mud should be considered a component
of the mortar mix.
were soaked in water for 24 hours prior to testing, according to
SANTOS
[18] studies.
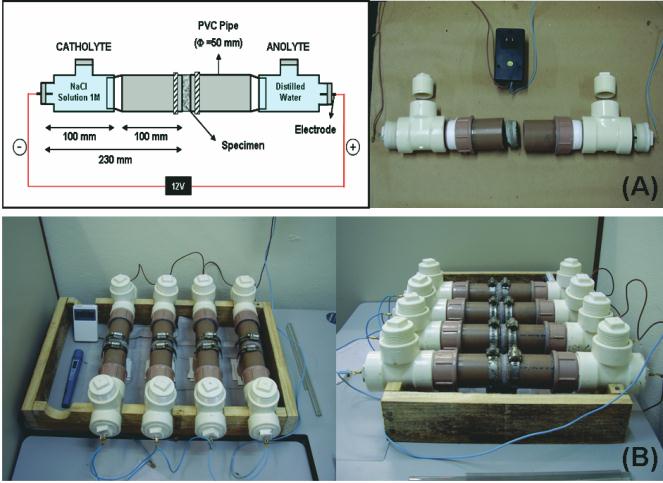
PVC cells were used, consisting of a 50 mm diameter “T” tube with
a top cover for output measurements and a side containing the
electrode, properly sealed to prevent loss of solution. The speci-
mens were placed at the interface between the two chambers,
and were also glued with a silicone-based adhesive. Thus, the ion
exchange between cells took place only through the body surface-
to-test exposed area. The test setup and its implementation are
illustrated in Figures 1a and 1b, respectively. A 12-Volt current was
applied to the system by means of electrodes positioned at the
ends of the cell, which were connected to copper wires from a
controlled voltage source.
The concentration of chlorides in the anolyte chamber (initially
free of chlorides) was analyzed at regular intervals during the
experiment using a portable digital conductivitimeter (CD-880,
Instrutemp). The chloride concentration was estimated based on
the correlation between this parameter and the electrical conduc-
tivity, as indicated in Figure 2. Conductivity values were refer-
enced to a temperature of 25°C, by considering an increase of
2% in the conductivity of the solution when the temperature rose
by one degree centigrade.
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Caracterização das matérias-primas
The Portland cement used in this work has a specific surface area
0.93 m
2
/g and its specific gravity is 3.11 Kg/dm
3
. The sand has a
specific surface area of 0.68 m
2
/g and its specific gravity is 2.70
Kg/dm
3
. According to Brazilian NBR 7211 standard, it is classified
Figure 1 – (A) Layout and assembly of the chloride migration test; (B) Chloride migration test apparatus
Figure 2 – Experimental correlation
between conductivity (at 25ºC) and
chloride concentration in the anolyte
chamber initially containing distilled water
y = 89,749x
R
2
= 0,986
0,0
5,0
10,0
15,0
20,0
25,0
0,00
0,05
0,10
0,15
0,20
0,25
Chloride Concentration (M)
Conductivity (mS/cm)

